[프로그래머스] 가사검색
업데이트:
2020 카카오 블라인드 코딩테스트 문제이다.
문제는 다음과 같다.



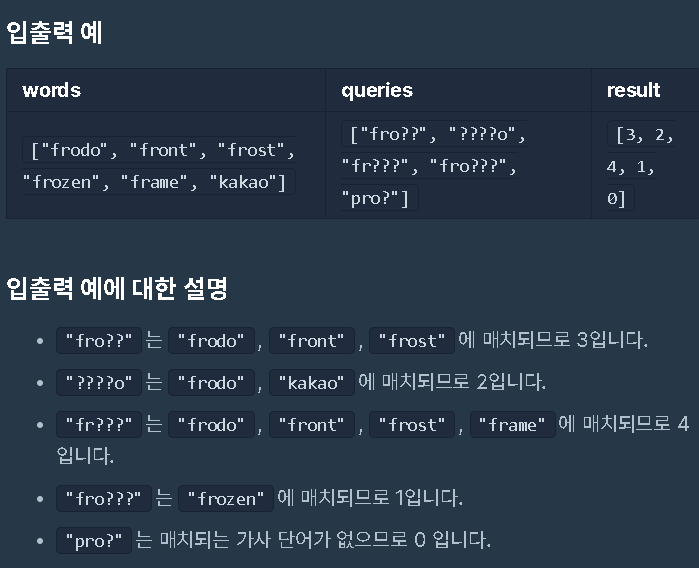
일단 이 문제는 난 실제 시험에선 절대 못풀었다. 이후 카카오에서 문제 설명을 해주면서 Trie자료구조를 사용해야 한다고 말을 하였고 그때 처음으로 Trie자료구조에 대해서 알게 되었다.
Trie 자료구조를 구현하여 비교하는 방법은 검색을 통해서 구현해보았다.
문제를 읽던 도중 제한사항을 보면 전체 키워드 길이 합이 100만을 넘지 않는다는 조건을 보고 해시를 사용해서 풀수 있지 않을까 해서 풀이를 생각해보니 길이에 따라서 해시로 풀 수도 있고 완탐으로 풀수도 있다고 생각을 했다.
그러다가 새로운 풀이 방법을 발견하였고, 그에 대한 풀이이다.
Trie풀이
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int NUM = 27;
int toNumber(char n) {
if (n == '?')
{
return 26;
}
return n - 'a';
}
struct TrieNode
{
TrieNode* children[NUM];
bool terminal;
int cnt;
TrieNode() :terminal(false), cnt(0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; ++i)
{
children[i] = NULL;
}
}
~TrieNode()
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++)
{
if (children[i])
{
delete children[i];
}
}
}
void insert(const char* key)
{
//키값이 널이라면
if (*key == 0)
{
terminal = true;
}
else
{
int next = toNumber(*key);
if (children[next] == NULL)
{
children[next] = new TrieNode();
}
children[next]->insert(key + 1);
}
}
void find(const char* key)
{
if (*key == 0)
{
cnt++;
return;
}
int next = toNumber(*key);
if (children[toNumber('?')] != NULL)
{
children[toNumber('?')]->find(key + 1);
}
if (children[next] != NULL)
{
children[next]->find(key + 1);
}
}
int getCnt(const char* key)
{
if (*key == 0)
{
return cnt;
}
int next = toNumber(*key);
if (children[next] == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return children[next]->getCnt(key + 1);
}
};
vector<int> solution(vector<string> words, vector<string> queries) {
vector<int> answer;
TrieNode Trie;
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {
Trie.insert(queries[i].c_str());
}
for (int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++) {
Trie.find(words[i].c_str());
}
for (int i = 0; i < queries.size(); i++) {
answer.push_back(Trie.getCnt(queries[i].c_str()));
}
return answer;
}
해시 풀이
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool match(string query, string word);
void create_map(vector<string> &words, unordered_map<string, int> &map);
vector<int> solution(vector<string> words, vector<string> queries) {
long long max_length = 0;
for (string word : words) {
max_length = max(max_length, word.length());
}
vector<int> answer;
if (max_length > 1000) { // 최대 갯수가 10000을 넘지 않을 것이기 때문에 완전탐색이 가능하다.
for (string query : queries) {
int num_matched = 0;
for (string word : words) {
if (match(query, word)) {
num_matched++;
}
}
answer.push_back(num_matched);
}
} else { // 갯수가 많아질 경우 해시맵을 뜻하는 unordered_map을 사용하여 비교한다.
unordered_map<string, int> map;
create_map(words, map);
for (string &query : queries) {
answer.push_back(map[query]);
}
}
return answer;
}
bool match(string &query, string &word) { // 완탐으로 비교하는 함수
if (query.length() != word.length()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < query.length(); ++i) {
if (query[i] != '?' && query[i] != word[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
void create_map(vector<string> &words, unordered_map<string, int> &map) { // 해시 생성
for (string word : words) {
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); ++i) {
map[word.substr(0, i) + string(word.length() - i, '?')]++;
map[string(i, '?') + word.substr(i)]++;
}
}
}
소스코드
이 외에도 제가 푼 문제들 소스코드는 다음 링크에 있습니다!!! 알고리즘 문제풀이

댓글남기기